

An EPG can be statically configured by an administrator in the APIC, Policies apply to EPGs, never to individual endpoints. Rather than configure and manage endpoints individually, they are placed in an EPG and are managed Management endpoint groups for out-of-band ( mgmtOoB) or in-band ( mgmtInB) access.ĮPGs contain endpoints that have common policy requirements such as security, virtual machine mobility (VMM), QoS, or LayerĤ to Layer 7 services. Layer 3 external outside network instance endpoint group ( l3extInstP) Layer 2 external outside network instance endpoint group ( l2extInstP) The ACI fabric can contain the following types of EPGs: Endpoint membership in an EPG can be dynamic or static.

Servers, virtual machines, network-attached storage, or clients on the EPGs are fullyĭecoupled from the physical and logical topology. Knowing the address of anĮndpoint also enables access to all its other identity details.
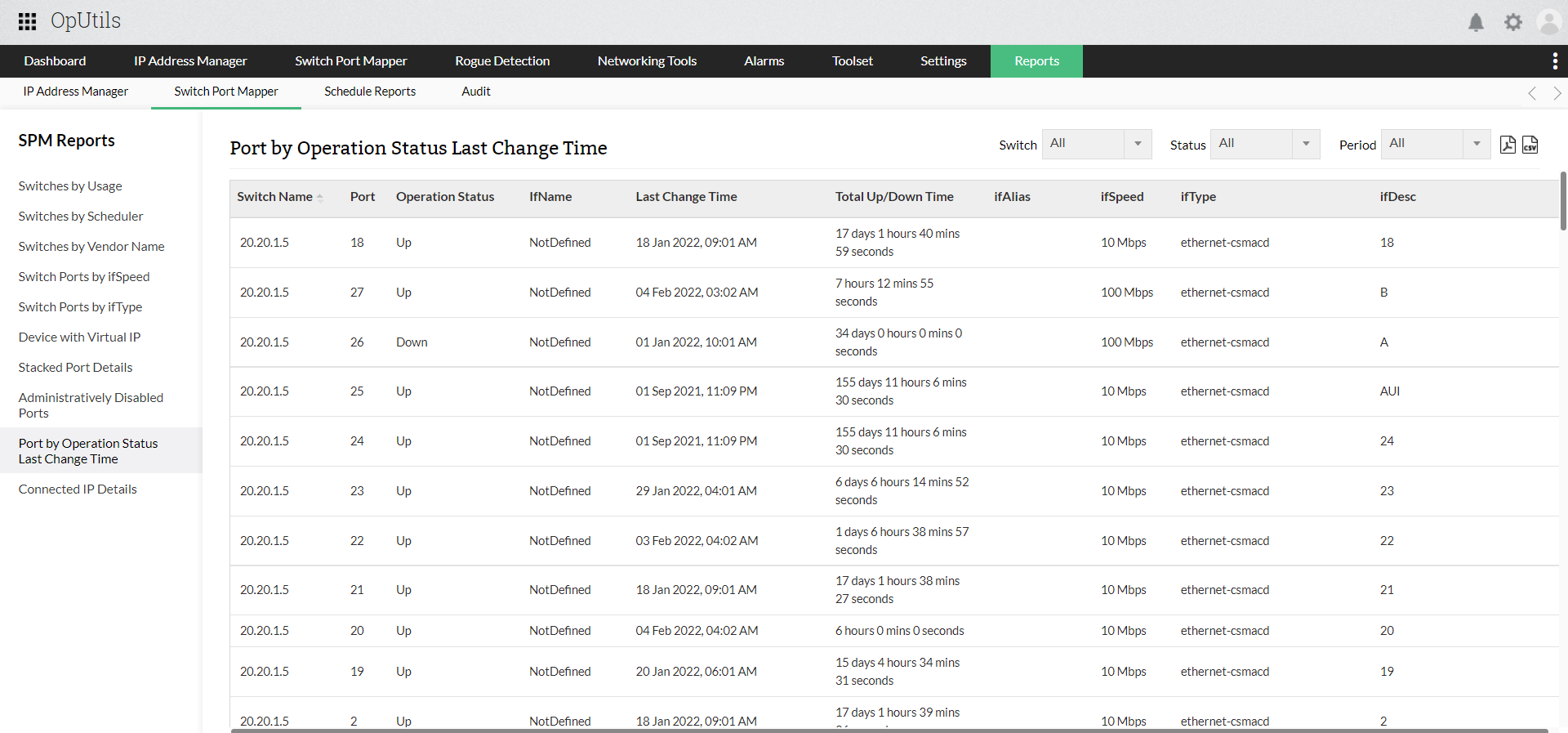
#SWITCH PORT MAPPING TEMPLATE PATCH#
Patch level), and can be physical or virtual. They have an address (identity), a location, attributes (such as version or Object that is a named logical entity that contains a collection of endpoints.Įndpoints are devices that are connected to the network directly or indirectly. The following figure shows where application EPGsĪre located in the management information tree (MIT) and their relation to other objects in the tenant. The endpoint group (EPG) is the most important object in the policy model. This chapter contains the following sections:
Intra-EPG Isolation Enforcement for Cisco AVS.Configuring Intra-EPG Isolation for VMware VDS or Microsoft Hyper-V Virtual Switch using the REST API.Configuring Intra-EPG Isolation for VMware VDS or Microsoft Hyper-V Virtual Switch using the NX-OS Style CLI.Configuring Intra-EPG Isolation for VMware VDS or Microsoft Hyper-V Virtual Switch using the GUI.Intra-EPG Isolation for VMware VDS or Microsoft Hyper-V Virtual Switch.Configuring Intra-EPG Isolation for Bare Metal Servers Using the REST API.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
